Product Category
- Standard Magnets
- Customs Magnets
- Magnetic Assmblies
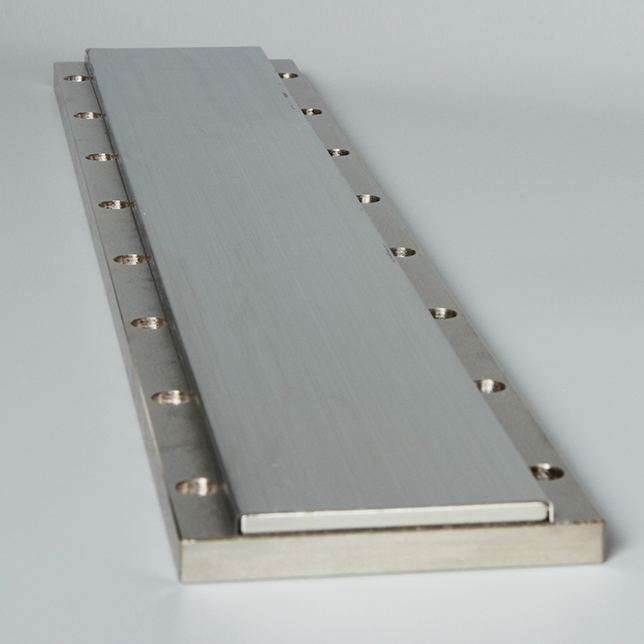
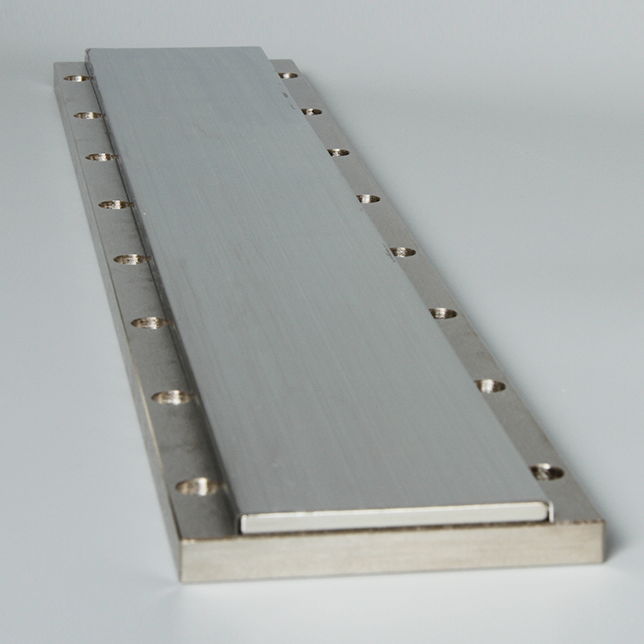
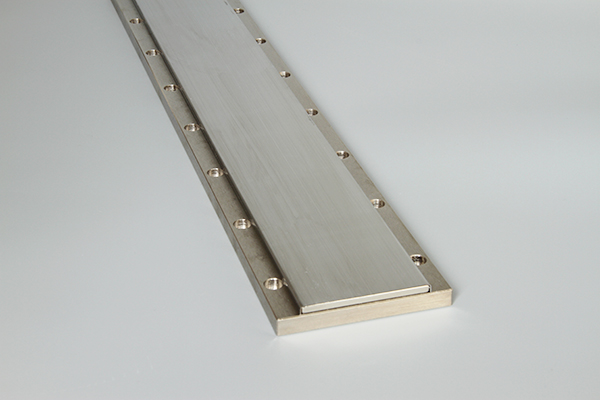
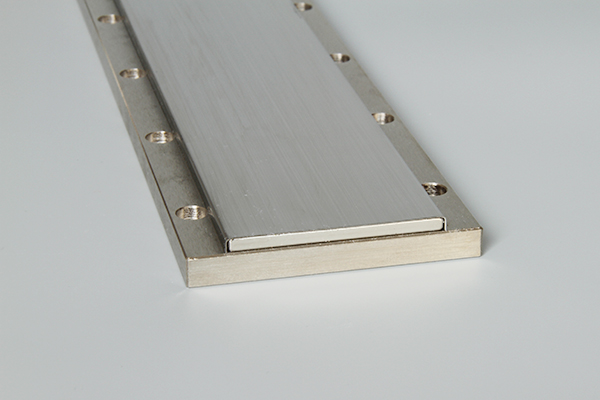
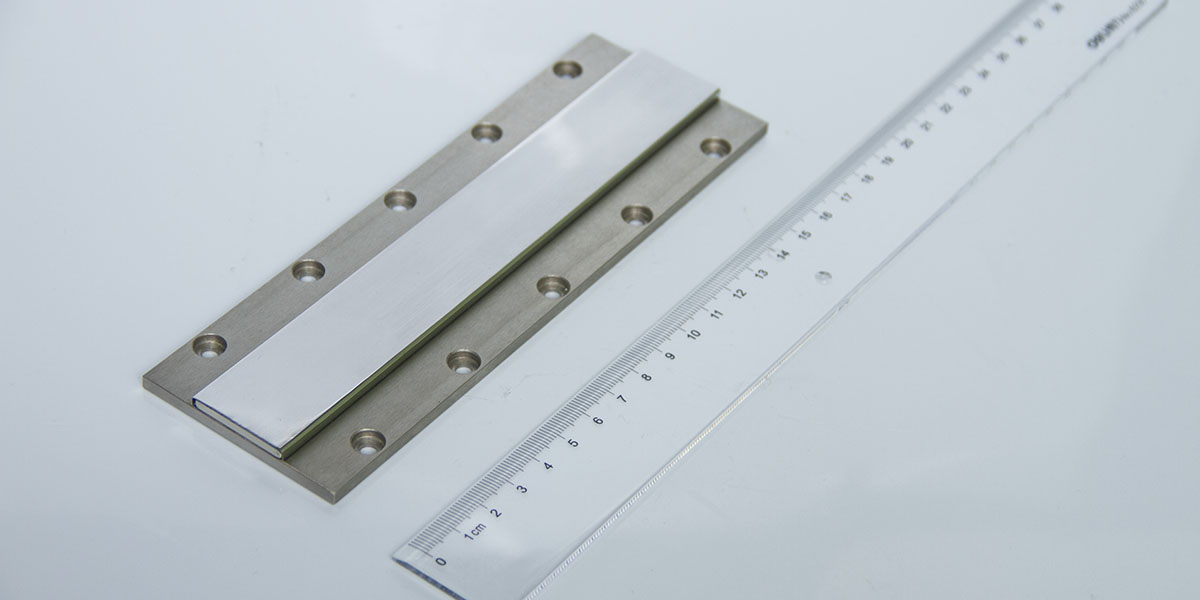
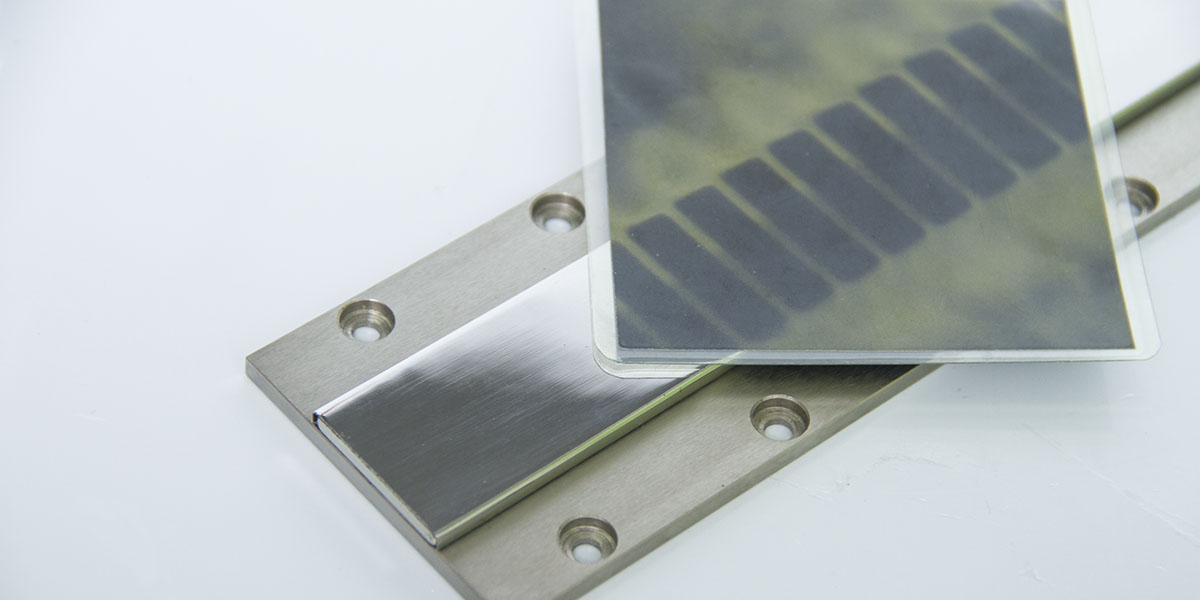
The linear motor is often described simply as a rotary motor that has been rolled out flat, and the principles of operation are the same. The forcer (rotor) is made up of coils of wires encapsulated in epoxy, and the track is constructed by placing magnets (usually high powerfull neodymium magnets) on steel.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
<template class="visibility">
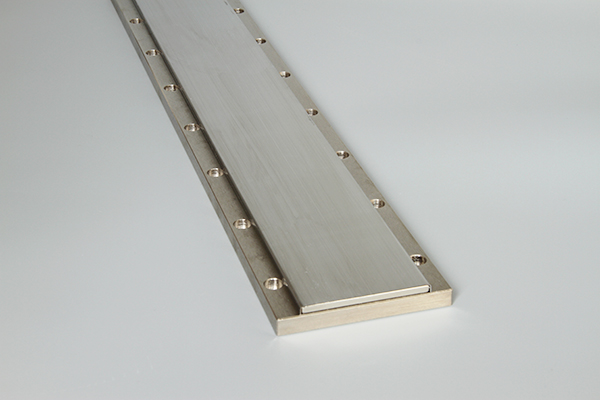
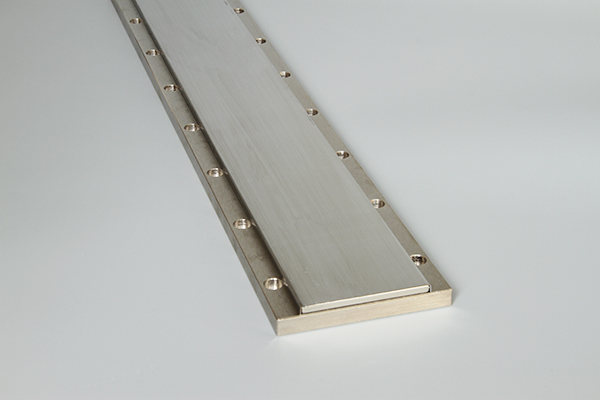
The linear motor is often described simply as a rotary motor that has been rolled out flat, and the principles of operation are the same. The forcer (rotor) is made up of coils of wires encapsulated in epoxy, and the track is constructed by placing magnets (usually high powerfull neodymium magnets) on steel.
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
















